Tensile testing
What's a tensile test and why's it important? Discover the importance of a tensile test in this article.
As the world of 3D printing continues to evolve, the applications and opportunities keep expanding exponentially. 3devo’s groundbreaking solution has provided engineers and researchers with the ability to design unique filaments for specific applications, ushering in new developments in the 3D printing field. The suitability of a material depends on its ability to fulfill mechanical requirements for a certain application, making tensile testing an important and fundamental testing method to properly determine the mechanical properties of the material and understand its performance over time. This article delves into the possibilities of performing tensile testing on 3D-printed specimens to assess the mechanical performance of the material.
What is a tensile test?
A tensile test is a basic mechanical measurement performed to determine the tensile properties of a material or component under a certain load. This test measures the force required to break a material specimen and the extent to which the specimen stretches or elongates to that breaking point. The deformation of the test sample serves to assess its ductility or brittleness, while simultaneously revealing critical properties like tensile strength, yield point, modulus of elasticity, elongation at break, elastic modulus, and toughness, which are crucial for designing and optimizing engineering components.
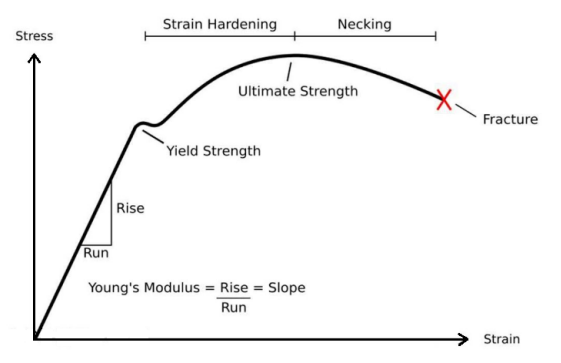
The strain-stress curve below depicts the different mechanical properties that can be obtained with this test.
How is the tensile test performed?
The most used and accepted standard for tensile testing is ASTM D638 – 14 (picture below), which can be used to test 3D-printed samples. To perform this experiment, the following steps must be taken:
- Sample preparation:
Common specimen shapes are dog-bone or dumbbell-shaped, with a narrower section in the middle called the "gage section" or "test section”. These dog-bone shape samples are 3D printed from the material which properties want to be evaluated.![ASTM D638 Dog-Bone Test Specimen [56]. | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331115553/figure/fig1/AS:726586131243010@1550243041321/ASTM-D638-Dog-Bone-Test-Specimen-56.jpg)
- Test setup
The specimen must be carefully aligned in the grips of the tensile testing machine. After that, the testing parameters must be set in the testing machine. - Test execution
Start by applying a small amount of preload to ensure that the specimen is securely seated in the grips. Once this has been secured, activate the testing machine which will start applying tensile force to the specimen. The machine will also record the load (force) and elongation (displacement) data continuously, and ultimately generate a stress-strain curve. - Data analysis
Analyze the stress-train curve that has been obtained from the experiment as this one provides valuable insights on the material’s mechanical behaviour.
In summary, tensile testing of 3D-printed samples is a crucial step in the material characterization process. It provides valuable insights into the mechanical properties of printed material, allowing optimization designs, selecting appropriate materials, and ensuring the reliability and performance of 3D-printed parts in various applications.
Tip:
Here you can find and download the STL of the ASTM D638 sample.